 Acupuncture
Acupuncture
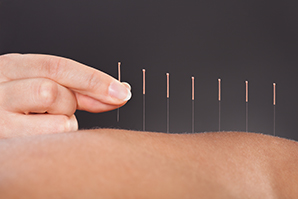
Acupuncture is a therapy that originated in China over 3,000 years ago. It involves inserting very thin single-use, disposable needles into the skin at various points throughout the body, stimulating nerves, muscles and connective tissue, as well as increasing blood flow and initiating one’s natural ability to heal oneself.
 Chinese Herbal Medicine
Chinese Herbal Medicine
Chinese herbal medicine uses plants and natural substances for therapy and medicinal purposes. It is amongst the world’s most ancient forms of healing. Acupuncturists rely primarily on the patient’s intake and pulse/tongue diagnosis in order to create a customized herbal formula blend, to address the various symptoms and complaints of the individual.
 Cupping
Cupping
Cupping is a healing technique used in many cultures. Small glass/plastic cups are used as suction devices and placed along an affected area on the skin in order to help disperse and break up stagnation/congestion of bodily fluids. The process itself helps to initiate an immune response, which improves circulation of blood and lymphatic flow. In dry cupping, the acupuncturist will simply suction cups on the skin for a short duration of time. In wet cupping, the practitioner will lancet the skin prior to applying single-use, disposable cups. This variation of cupping helps to draw out old and stagnant blood, which is impeding proper blood flow.
 Moxibustion
Moxibustion
Moxibustion is a form of heat therapy in which Chinese mugwort (Artemesiaargyi or A.vlugaris) is burned on or lit very close to the skin’s surface. It helps to warm and invigorate the flow of qi and blood within the body as well as to help reignite the body’s natural yang/fire energy.
 Guasha
Guasha
Guasha is a traditional healing technique of East Asia and translates as “scraping the redness.” It consists of using an instrument (typically a smooth piece of jade, buffalo horn or Chinese soup spoon) accompanied with oil, on the affected area. The tool is scraped across the skin in order to intentionally create an immune response, helping to regulate the blood just beneath the skin.

